Imaging Services
Methodist McKinney Hospital is your go-to medical facility for high-quality imaging services. Our compassionate team of medical experts provides the best possible care for every patient.
Why Choose Us:

Baseline Screenings
Patient Education
MRI
An MRI—which stands for magnetic resonance imaging—is a type of imaging technology that combines a magnetic field with radio waves to create detailed pictures of organs and tissue. These detailed images allow our doctors to customize care for every patient who walks through our doors.
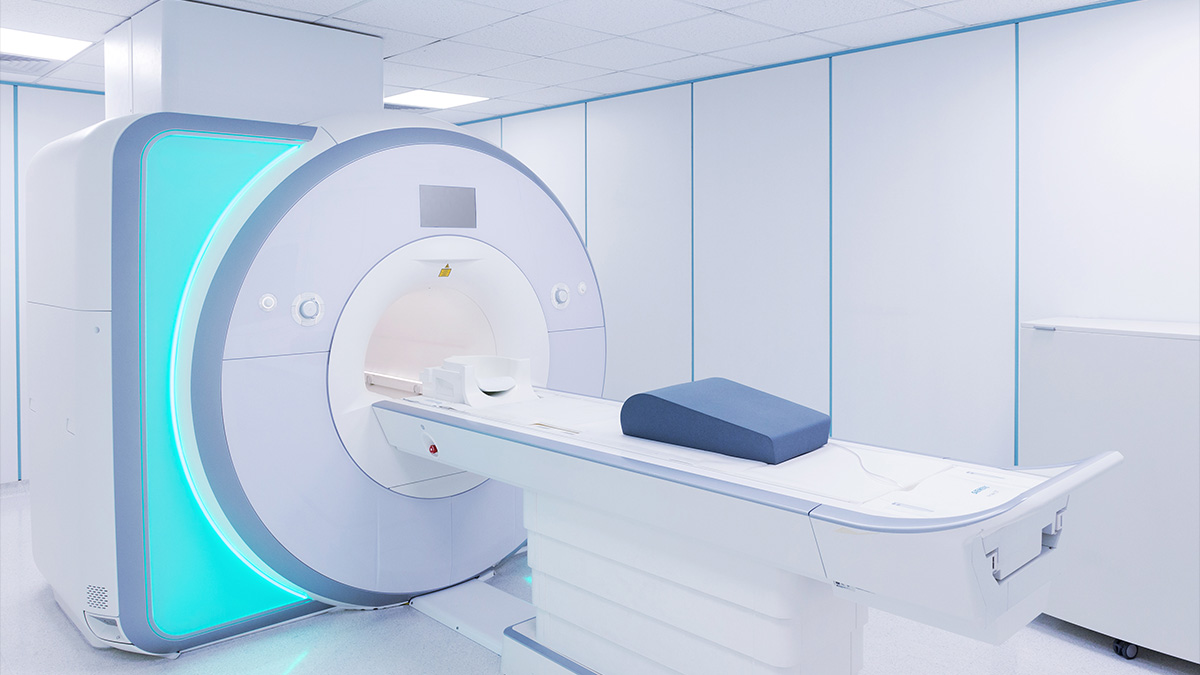
Unlike previous MRI technology, the Signa Explorer Lift allows patients to move during the scan without sacrificing image quality. Patients can rest easy knowing they won’t have to endure multiple retakes, which means less time spent in a confined space.
Additional MRI Benefits:
- Scan time decreased by up to 40%
- Scans are significantly quieter to increase patient comfort
- Dramatic increase in image resolution, providing superior quality scans
Our sedated MRI option is the perfect solution for patients who are:
- Anxious
- Claustrophobic
- Unable to remain still during the scan due to pain or discomfort
We can perform a sedated MRI on any region of the body. Conscious sedation and General IV sedation are administered and monitored by an anesthesiologist. For minimal sedation, oral medications can be prescribed by the patient’s referring physician and brought with the patient to take prior to study.
Advantages of sedated MRIs:
- Extremely accurate imaging
- Improved patient experience
- Minimal time spent in MRI suite
A MRI Brain Scan is one of the most detailed imaging tests for the brain. It uses magnetic fields and radiofrequency waves (no radiation) to create high-resolution pictures of brain structures.
Why it is done:
Screenings are performed to evaluate tumors and TIA, which is a mini stroke. TIA happens when blood flow to part of the brain is briefly blocked. The scan shows the brain tissue and brain parenchyma.
Scan is 20-30 minutes.
A Head and Neck Vascular Screen is an imaging study that looks at the blood vessels supplying the brain, head, and neck.
Why it is done:
To check for conditions that affect blood flow, such as:
- Carotid artery stenosis- narrowing, often from plaque buildup
- Aneurysms- weakened, bulging vessels
- Arteriovenous malformations
- Vessel dissection- tear in the vessel wall
- Vascular blockages or clots that could lead to stroke
MRI uses magnetic fields to show vessels without radiation. It is often ordered if you have risk factors for vascular disease such as high blood pressure, smoking or family history.
Scan is 30 minutes.
A MRA Brain Artery Scan (Circle of Willis) is a specialized Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) study that focuses on the blood vessels at the base of the brain.
Why is it done:
To check for aneurysms, detect stenosis or occlusions, vascular malformations, and assessing blood flow patterns.
This is a full study of the arteries, Circle of Willis:
- Internal carotid arteries
- Anterior cerebral arteries
- Middle cerebral arteries
- Posterior cerebral arteries
- Communicating arteries
Scan is 15 minutes long.
- Advanced Motion Correction Technology
-
Unlike previous MRI technology, the Signa Explorer Lift allows patients to move during the scan without sacrificing image quality. Patients can rest easy knowing they won’t have to endure multiple retakes, which means less time spent in a confined space.
Additional MRI Benefits:
- Scan time decreased by up to 40%
- Scans are significantly quieter to increase patient comfort
- Dramatic increase in image resolution, providing superior quality scans
- Sedated MRI
-
Our sedated MRI option is the perfect solution for patients who are:
- Anxious
- Claustrophobic
- Unable to remain still during the scan due to pain or discomfort
We can perform a sedated MRI on any region of the body. Conscious sedation and General IV sedation are administered and monitored by an anesthesiologist. For minimal sedation, oral medications can be prescribed by the patient’s referring physician and brought with the patient to take prior to study.
Advantages of sedated MRIs:
- Extremely accurate imaging
- Improved patient experience
- Minimal time spent in MRI suite
- Brain Scan
-
A MRI Brain Scan is one of the most detailed imaging tests for the brain. It uses magnetic fields and radiofrequency waves (no radiation) to create high-resolution pictures of brain structures.
Why it is done:
Screenings are performed to evaluate tumors and TIA, which is a mini stroke. TIA happens when blood flow to part of the brain is briefly blocked. The scan shows the brain tissue and brain parenchyma.
Scan is 20-30 minutes.
- Head & Neck Vascular Scan
-
A Head and Neck Vascular Screen is an imaging study that looks at the blood vessels supplying the brain, head, and neck.
Why it is done:
To check for conditions that affect blood flow, such as:
- Carotid artery stenosis- narrowing, often from plaque buildup
- Aneurysms- weakened, bulging vessels
- Arteriovenous malformations
- Vessel dissection- tear in the vessel wall
- Vascular blockages or clots that could lead to stroke
MRI uses magnetic fields to show vessels without radiation. It is often ordered if you have risk factors for vascular disease such as high blood pressure, smoking or family history.
Scan is 30 minutes.
- Brain Artery Scan, Circle of Willis
-
A MRA Brain Artery Scan (Circle of Willis) is a specialized Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) study that focuses on the blood vessels at the base of the brain.
Why is it done:
To check for aneurysms, detect stenosis or occlusions, vascular malformations, and assessing blood flow patterns.
This is a full study of the arteries, Circle of Willis:
- Internal carotid arteries
- Anterior cerebral arteries
- Middle cerebral arteries
- Posterior cerebral arteries
- Communicating arteries
Scan is 15 minutes long.
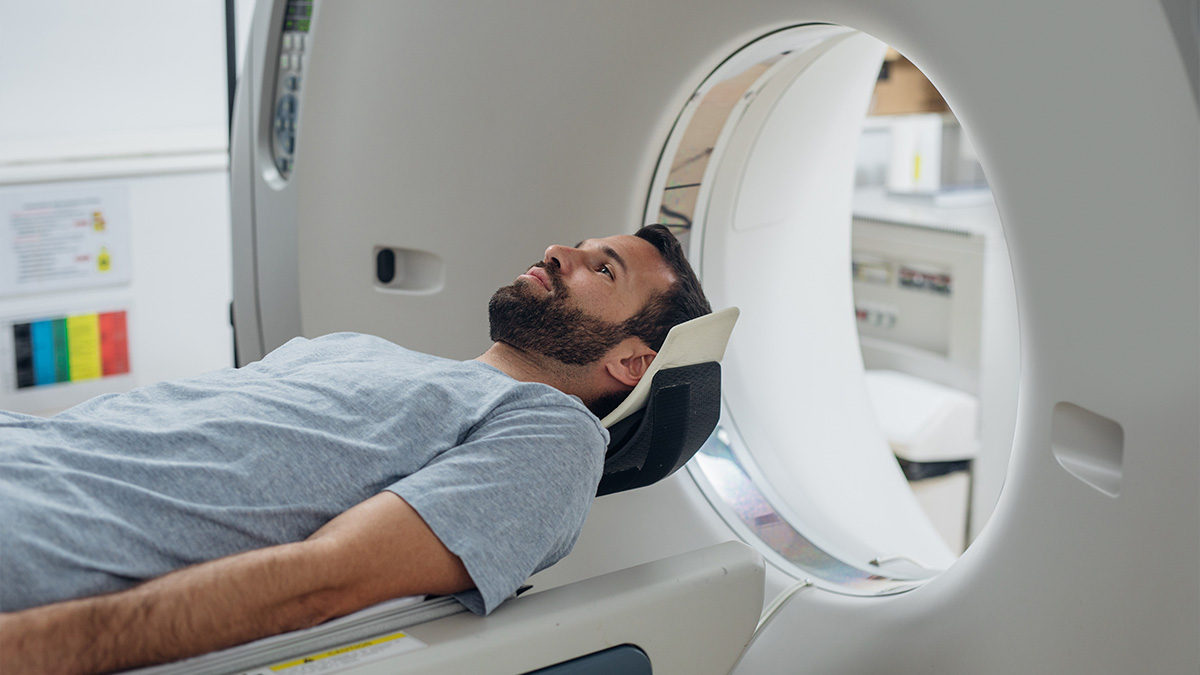
CT
Standard CT Scan
A standard CT scan—also known as a CAT scan or Computed Tomography scan—provides detailed images of internal organs, bones, blood vessels, and tissues. CT scans show more detailed images than a generic X-ray. Here’s how it works:
- A narrow X-ray beam circles around the targeted body part, providing a series of images from various angles
- A computer uses this information to create a cross-sectional 2D picture
- Multiple scans can be stacked on top of each other to create one 3D image
Most CT scans will take 30 minutes or less to complete. As patients lie on a table inside the round CT machine, X-rays rotate around their bodies to take detailed images. The machine will create a whirring or buzzing noise as it rotates. Any movement inside the CT scanner can blur images, so patients must remain still until scans are completed.
Equipped with twin spiral dual-energy, CareDose 4D, and single-click readiness technologies, our Low Dose 64 Slice Siemens Somatom CT scanner accelerates and simplifies the CT scanning process.
The twin spiral dual-energy technology enables the CT scanner to zoom in on small details that standard CT scanners don’t always detect. It also helps physicians examine scans with greater accuracy so they can provide customized treatment options.
The CareDose 4D technology allows us to tailor radiation doses based on each patient’s size and the body part being scanned. It also protects medical personnel and patients from unnecessary radiation exposure.
With the single-click readiness technology, doctors can receive high-quality scans with the press of a button.
Additional benefits of the 64 Slice CT scanner include:
- Enhanced imaging
- Shorter scan time
- Quieter operation
- Optimized contrast
- Tailored radiation doses
- Minimal radiation exposure
A CT calcium score is a non-invasive heart scan that detects early coronary artery disease and predicts future heart attacks. The higher your calcium score, the higher your risk of developing heart disease and/or having a heart attack.
If you fall into two or more of the following risk categories, you should get a calcium score.
- Family history of coronary artery disease
- High cholesterol
- High triglycerides
- Smoking
- Hypertension
- Diabetes mellitus
- Obesity
You can get your calcium score with a simple imaging scan at Methodist McKinney Hospital. An appointment is required and are available between 8:00 a.m. and 5:00 p.m. Monday through Friday. Please call 972-569-2717 to schedule. Since CT calcium scores aren’t covered by insurance, we offer a competitive self-pay option of $125.
A CT Lung Scan is a detailed X-ray test that creates cross-sectional images of your lungs and chest.
Why it is done:
Screenings are performed to detect early lung cancer, especially people ages 50-80 with a minimum smoking habit of 20pack/year history.
Screen looks for infections, inflammation, scarring and nodules.
Nodules or masses and pleural problems can be detected with this scan.
Scan is 10 minutes.
A CT Torso Baseline scan provides a starting-point set of images of your chest, abdomen, and pelvis. This scans from your shoulders through pelvis (not including coronary).
Why it is done:
Screening is performed to detect abnormalities in the:
- Chest- lungs, heart, lymph nodes.
- Abdomen- liver, gallbladder, pancreas, kidneys, spleen, intestines.
- Pelvis- bladder, reproductive organs, bowel.
- Bones- ribs, spine, pelvis
Scan is 5 minutes long.
- CT Technology
-
Equipped with twin spiral dual-energy, CareDose 4D, and single-click readiness technologies, our Low Dose 64 Slice Siemens Somatom CT scanner accelerates and simplifies the CT scanning process.
The twin spiral dual-energy technology enables the CT scanner to zoom in on small details that standard CT scanners don’t always detect. It also helps physicians examine scans with greater accuracy so they can provide customized treatment options.
The CareDose 4D technology allows us to tailor radiation doses based on each patient’s size and the body part being scanned. It also protects medical personnel and patients from unnecessary radiation exposure.
With the single-click readiness technology, doctors can receive high-quality scans with the press of a button.
Additional benefits of the 64 Slice CT scanner include:
- Enhanced imaging
- Shorter scan time
- Quieter operation
- Optimized contrast
- Tailored radiation doses
- Minimal radiation exposure
- Calcium Score
-
A CT calcium score is a non-invasive heart scan that detects early coronary artery disease and predicts future heart attacks. The higher your calcium score, the higher your risk of developing heart disease and/or having a heart attack.
If you fall into two or more of the following risk categories, you should get a calcium score.
- Family history of coronary artery disease
- High cholesterol
- High triglycerides
- Smoking
- Hypertension
- Diabetes mellitus
- Obesity
You can get your calcium score with a simple imaging scan at Methodist McKinney Hospital. An appointment is required and are available between 8:00 a.m. and 5:00 p.m. Monday through Friday. Please call 972-569-2717 to schedule. Since CT calcium scores aren’t covered by insurance, we offer a competitive self-pay option of $125.
- Lung Scan
-
A CT Lung Scan is a detailed X-ray test that creates cross-sectional images of your lungs and chest.
Why it is done:
Screenings are performed to detect early lung cancer, especially people ages 50-80 with a minimum smoking habit of 20pack/year history.
Screen looks for infections, inflammation, scarring and nodules.
Nodules or masses and pleural problems can be detected with this scan.Scan is 10 minutes.
- Torso Scan
-
A CT Torso Baseline scan provides a starting-point set of images of your chest, abdomen, and pelvis. This scans from your shoulders through pelvis (not including coronary).
Why it is done:
Screening is performed to detect abnormalities in the:
- Chest- lungs, heart, lymph nodes.
- Abdomen- liver, gallbladder, pancreas, kidneys, spleen, intestines.
- Pelvis- bladder, reproductive organs, bowel.
- Bones- ribs, spine, pelvis
Scan is 5 minutes long.

CT
Standard CT Scan
A standard CT scan—also known as a CAT scan or Computed Tomography scan—provides detailed images of internal organs, bones, blood vessels, and tissues. CT scans show more detailed images than a generic X-ray. Here’s how it works:
- A narrow X-ray beam circles around the targeted body part, providing a series of images from various angles
- A computer uses this information to create a cross-sectional 2D picture
- Multiple scans can be stacked on top of each other to create one 3D image
Most CT scans will take 30 minutes or less to complete. As patients lie on a table inside the round CT machine, X-rays rotate around their bodies to take detailed images. The machine will create a whirring or buzzing noise as it rotates. Any movement inside the CT scanner can blur images, so patients must remain still until scans are completed.
CT Technology
The twin spiral dual-energy technology enables the CT scanner to zoom in on small details that standard CT scanners don’t always detect. It also helps physicians examine scans with greater accuracy so they can provide customized treatment options.
The CareDose 4D technology allows us to tailor radiation doses based on each patient’s size and the body part being scanned. It also protects medical personnel and patients from unnecessary radiation exposure.
With the single-click readiness technology, doctors can receive high-quality scans with the press of a button.
Additional benefits of the 64 Slice CT scanner include:
- Enhanced imaging
- Shorter scan time
- Quieter operation
- Optimized contrast
- Tailored radiation doses
- Minimal radiation exposure
CT Calcium Score
If you fall into two or more of the following risk categories, you should get a calcium score.
- Family history of coronary artery disease
- High cholesterol
- High triglycerides
- Smoking
- Hypertension
- Diabetes mellitus
- Obesity
You can get your calcium score with a simple imaging scan at Methodist McKinney Hospital. An appointment is required and are available between 8:00 a.m. and 5:00 p.m. Monday through Friday. Please call 972-569-2717 to schedule. Since CT calcium scores aren’t covered by insurance, we offer a competitive self-pay option of $125.
CT Lung Scan
Why it is done:
Screenings are performed to detect early lung cancer, especially people ages 50-80 with a minimum smoking habit of 20pack/year history.
Screen looks for infections, inflammation, scarring and nodules.
Nodules or masses and pleural problems can be detected with this scan.
Scan is 10 minutes.
CT Torso Scan
Why it is done:
Screening is performed to detect abnormalities in the:
- Chest- lungs, heart, lymph nodes.
- Abdomen- liver, gallbladder, pancreas, kidneys, spleen, intestines.
- Pelvis- bladder, reproductive organs, bowel.
- Bones- ribs, spine, pelvis
Scan is 5 minutes long.
Ultrasound
Ultrasounds—also known as sonograms and sonography—provide high-quality images of a patient’s internal body structures. The ultrasound machine works by directing high-frequency sound waves at the internal body structures being examined, and the sounds or echoes are recorded to create images the doctor will view on a monitor screen. Ultrasounds are a safe non invasive method to view internal organs without the use of radiation.
Special Instructions
Some Ultrasound examinations require special preparation beforehand, such as:
- Not being permitted to eat for six hours before an abdominal scan
- Undergoing a full bladder scan before a pelvic examination
Ask your doctor or the ultrasound technologist if any special preparation is required for your scan.
Below are some commonly performed procedures:
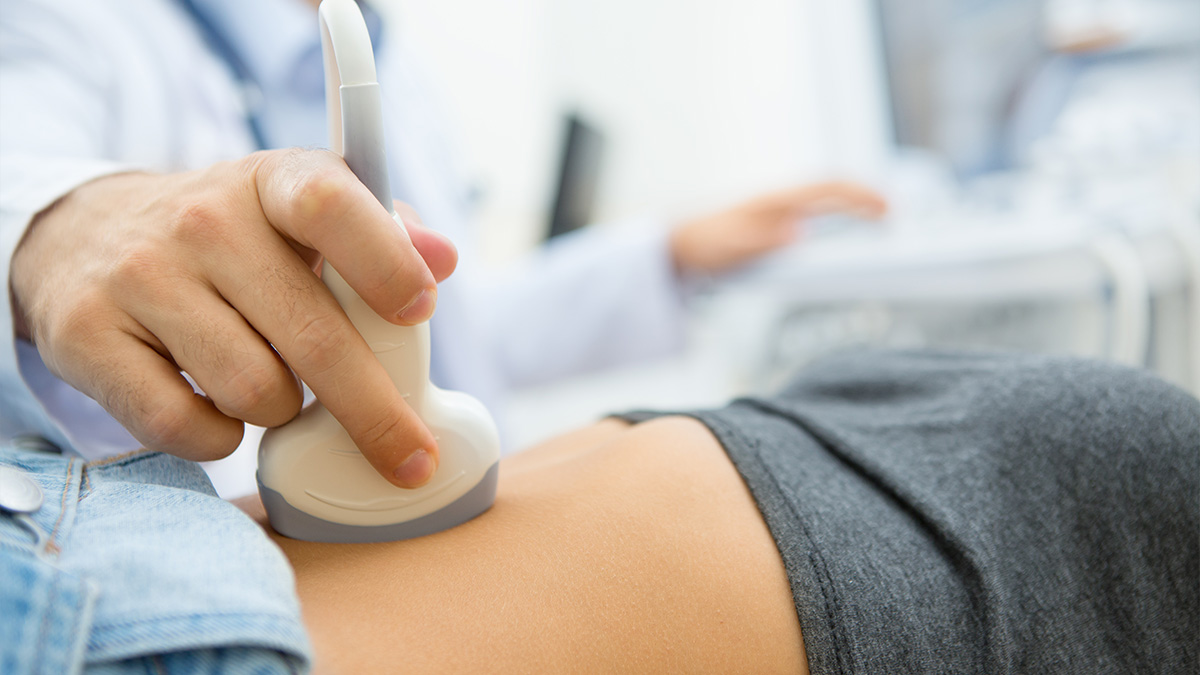

A Carotid Artery Bilateral Scan is a noninvasive ultrasound test that looks at the carotid arteries in both sides of your neck. These arteries supply blood from the heart to the brain.
Why it is done:
To detect narrowing or blockages caused by plaque (atherosclerosis) and assess risk of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
An ultrasound technologist places gel on your neck and moves an ultrasound probe over the carotid arteries. The scan uses doppler ultrasound to measure blood flow and detect turbulence from narrowing. Both left and right arteries are scanned. The scan shows narrowing, plaque characteristics, and blood flow velocity, which helps estimate how much the artery is blocked.
Scan is 15-20 minutes long.
An Aorta Scan via ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test used to look at the aorta, the largest blood vessel in the body that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
Why is it done:
The Aorta Scan is performed to check for an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), which is a bulging or widening of the vessel wall.
A technician applies gel on the abdomen and uses an ultrasound probe over the area to produce sound waves that create real-time images of the aorta on a screen.
This scan shows:
- Aorta size and shape
- Presence of aneurysms, narrowing (stenosis) or blockages
- How the blood is flowing through the aorta
The screen is typically ordered on previous or current smokers, those with family history of aortic aneurysm, those with symptoms of pulsating abdominal mass or unexplained circulation issues.
This is an 8 hour fasting test.
Scan is 15-20 minutes long.
This scan combines the Carotid Artery and Aorta scan into one study. It evaluates the arteries from the neck to the brain, as well as the heart to the rest of the body.
Details of each individual test can be found separately.
Scan is 30-40 minutes.
- US Carotid Artery Bilateral Scan
-
A Carotid Artery Bilateral Scan is a noninvasive ultrasound test that looks at the carotid arteries in both sides of your neck. These arteries supply blood from the heart to the brain.
Why it is done:
To detect narrowing or blockages caused by plaque (atherosclerosis) and assess risk of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
An ultrasound technologist places gel on your neck and moves an ultrasound probe over the carotid arteries. The scan uses doppler ultrasound to measure blood flow and detect turbulence from narrowing. Both left and right arteries are scanned. The scan shows narrowing, plaque characteristics, and blood flow velocity, which helps estimate how much the artery is blocked.
Scan is 15-20 minutes long.
- US Aorta Scan
-
An Aorta Scan via ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test used to look at the aorta, the largest blood vessel in the body that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
Why is it done:
The Aorta Scan is performed to check for an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), which is a bulging or widening of the vessel wall.
A technician applies gel on the abdomen and uses an ultrasound probe over the area to produce sound waves that create real-time images of the aorta on a screen.
This scan shows:
- Aorta size and shape
- Presence of aneurysms, narrowing (stenosis) or blockages
- How the blood is flowing through the aorta
The screen is typically ordered on previous or current smokers, those with family history of aortic aneurysm, those with symptoms of pulsating abdominal mass or unexplained circulation issues.
This is an 8 hour fasting test.
Scan is 15-20 minutes long. - US Carotid Artery and Aorta Combination Scan
-
This scan combines the Carotid Artery and Aorta scan into one study. It evaluates the arteries from the neck to the brain, as well as the heart to the rest of the body.
Details of each individual test can be found separately.Scan is 30-40 minutes.
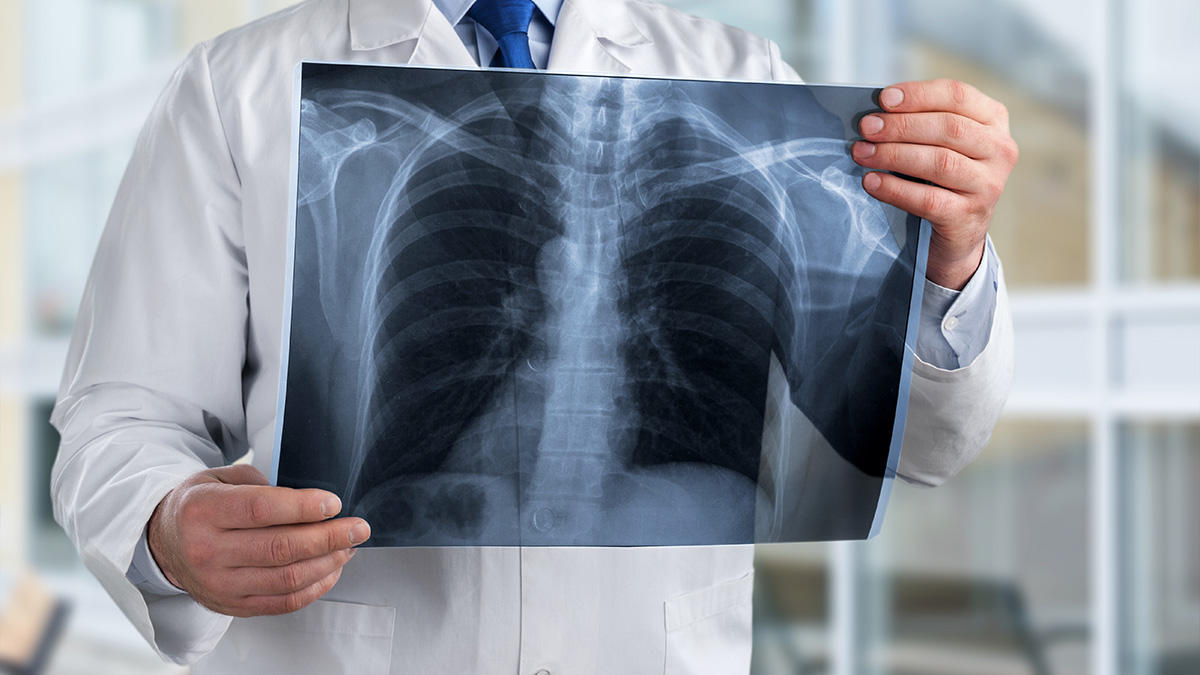
X-Ray
X-rays use electromagnetic waves to create detailed, black and white pictures of the inside of your body. Bones appear white, fat and soft tissue appear gray, and the lungs appear black. The main purpose of X-ray technology is to identify broken bones. However, it’s also used to detect conditions such as pneumonia and breast cancer. Since X-rays emit small amounts of radiation, patients are required to wear a lead shield to protect certain body parts from it.
Our Radiology Team
Our radiology department’s staff consistently receives high marks in patient satisfaction and awards for quality care. They’re willing to do whatever it takes to produce optimal results and give patients the best experience possible.
Department Hours & Information
Monday-Friday: 7a.m.-7p.m.
Saturday-Sunday: 7a.m. – 5p.m.
Call 1.972.569.2717 with any questions or to schedule an appointment.
For Physicians, please click here to access our remote PACS portal. You must be set up with an account prior to logging in.



